Best High Protein Foods:

This list shows which foods are high in proteins. The protein from our food provides essential amino acids. Amino Acids are used by the body to build new proteins and repair the muscles, repair the bone, skin, organs and blood. Without protein, cuts and abrasions will not heal quickly, muscles will not grow and the blood doesn’t clot correctly. Your body needs proteins for growth and to build hormones, antibodies and the enzymes that regulate the chemical reactions within the body.Though protein food is not a high source of energy, it is necessary, in right amounts, for proper functioning of our bodies.
The best proteins are those that are vegan or plant-based sources (except soy and other GMO crops)
The List of the Best High Protein Foods

prioritized in order of nutritional value are:

WHEY
Whey (supplement found in health food stores). The best are Protein Whey from the milk of free-ranging grass-fed “happy” cows from New Zealand, The milk should not come from cows fed with grains or GMO products and should not be injected with bovine growth hormones or medication (eg antibiotics).
Whey and casein proteins from milk have the greatest bioavailability when compared to popular protein alternatives, including egg, soy, and all other vegetable proteins.
Undenatured whey protein is water soluble, thus is quickly digested in the body, earning it the “fast protein” title. It’s amino acids are quickly available in large quantities soon after consumption (30-45 minutes).
Casein is water insoluble and coagulates, resulting in a slow-release mechanism of amino acids over a longer period of time. Consumption of a casein supplement results in slower availability of amino acids, which is why it is labeled a “slow protein.” Although superior to egg, soy, and other vegetable protein, casein proteins are too slowly absorbed to take advantage of the greater anabolic state of the body that occurs for about 90 minutes after workout (Campbell et al., 2007; Wilson and Wilson, 2006).
Campbell B, Kreider RB, Ziegenfuss T, La Bounty P, Roberts M, Burke D, Landis J, Lopez H, Antonio J International Society of Sports Nutrition position stand: protein and exercise. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2007 Sep 26; 4():8.
Wilson J, Wilson GJ. Contemporary issues in protein requirements and consumption for resistance trained athletes. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2006 Jun 5; 3():7-27.
If you are interested in a good organic whey protein shake, contact us.


Best Clean Vegan Protein to make a Smoothie without a Animal Protein Powder
These clean protein from plant sources make an excellent smoothie drink alternative to animal protein powders:
- Oats + Spinach
- Hemp seeds + Kale
- Pumpkin seeds + Oats
- Spinach + Quinoa
- Almond Butter + Chia Seeds
- Chia seeds + Kale
Legumes: peas, beans & lentils
Beans are one type of legume. They don’t provide all of the essential amino acids and are therefore considered an “incomplete” source of protein. Although this was considered a potential problem decades ago, now it’s understood that eating a normal varied diet will easily help you meet all of your amino-acid requirements. In other words, the fact that beans are an “incomplete” source of protein doesn’t make them any less beneficial than “complete” sources. Different beans provide different amounts of protein. Adzuki beans, a small red bean used in Japanese dishes, contain 17 g of protein in one cooked cup. A cup of black beans contains 15 g of protein; a cup of kidney beans contains 13 g of protein, and a cup of chickpeas contains 12 g of protein.
Lentils are another type of legume. These small, lens-shaped legumes can be eaten as a side dish or added to stews and soups. Like beans, lentils don’t contain all of the essential amino acids, although they are still considered an excellent source of protein if you eat a varied diet. One cup of cooked lentils contains 18 g of protein.
Peanuts — despite their name and many people’s beliefs that they are a nut — are actually a type of legume. One cup of raw Virginia peanuts contains 36 g of protein.
Peas also, fall into the legume category. Peas are available whole and split and can be eaten as a side dish or added to soups. One cup of cooked whole green peas contains 8 g of protein. One cup of cooked split peas contains 16 g of protein.
If you have a choice between legumes like beans versus grains, it is better to eat beans because the starches in them turn into sugars slower than that of grains.

Soy
Soy products: tofu, soy milk is NOT recommended by us because 90% of the crop production are now GMO) although many similar articles recommend this unhealthy food. The only exception is fermented soy products eg fermented tofu (usually in bottles from Chinese health food stores), miso, tempeh and natto. One cup of cooked mature soybeans, (if you can find organic non-GMO soya beans) contains 28 g of protein. One cup of green organic soybeans, also known as edamame, contains 22 g of protein. Soybeans can be made into tofu, commonly used as a meat substitute in vegetarian dishes. A 1-cup serving of tofu contains 40 g of protein.

Grains: breads, pasta, brown rice (preferably whole grains with minimal processing)
Amaranth – 6.10 grams*
Barley, hulled – 5.62 grams*
Brown rice – 3.38 grams*
Buckwheat – 5.96 grams*
Kamut Khorasan Wheat – 6.54 grams*
Millet – 4,96 grams*
Oats, rolled – 5.92 grams*
Quinoa – 6.35 grams
Rye – 4.65 grams*
Sorghum – 5.09 grams*
Spelt – 6.56 grams*
Wheat – 6.93 grams*
Wheat, bulgur – 5.53 grams*
Wild rice – 6.63 grams*
* Based on 45g uncooked grains
The healthiest grains are barley (if you are not gluten sensitive), amaranth or quinoa.

Nuts and Seeds
Nuts & Seeds: almonds, oatmeal, walnuts, cashews, peanuts, etc / pumpkin, sunflower, sesame & others. Pistachios are a practical protein choice if you’re on the move. Around 50 pistachio nuts will provide 6g of protein, plus sodium and potassium, the electrolytes lost in sweat during exercise.
Almonds – 15% carbs, 13% protein (6g / per handful), 72% fat
Cashews – 22% carbs, 11.5% protein (6g / per handful) , 66.5% fat
Peanut Butter – 13% carbs, 17% protein (8gm / 2tbsp), 70% fat
Walnuts – 8.5% carbs, 8% protein (6g / per handful), 83.5% fat
Pecans – 8% carbs, 5% protein (6g / per handful) , 87% fat
Flax seeds – 22% carbs, 12% protein (6g / per handful), 66% fat
Pumpkin seeds – 13% carbs, 16% protein ( (6g / per handful)), 71% fat
Sesame seeds – 17% carbs, 11% protein (6g / per handful) , 72% fat
Sunflower seeds – 17% carbs, 11.5% protein (6g / per handful) , 71.5% fat

High Protein Vegetables
Vegetables: potatoes, broccoli, spinach and other vegetables (including frozen veggies)
Peas – Each half-cup contains three and a half grams of protein. Try them in this creamy fresh pea soup with mint.
Spinach – You’ll find three grams of protein in a half cup of spinach. Get your fill with one of these yummy spinach smoothies. 5g / per serving (180g)
Baked Potato – Another stealth source of protein? Potatoes! A medium-sized one contains three grams.
NOTE: Potatoes are high in starch which is quickly converted into sugar so should be eliminated if possible. If you can’t do without it, reduce intake and add healthy fats on it like butter, coconut oil or olive oil.
Broccoli – Broccoli’s not just filled with fiber (2.6 grams per half cup)—it’s also a great source of protein, with two grams per serving. Up your intake by sampling one of our four favorite broccoli recipes. 5g protein / per serving (180g)
Brussels Sprouts – These little green guys get a bad rap, but they’re actually nutritional superstars: Each half cup packs two grams of protein, along with 247 milligrams of potassium and 110 micrograms of vitamin K.
Cauliflower – 5g protein / per serving (180g)
Corn – OK, we know that corn is technically a grain. But you can find it in the produce aisle—and you’ll be glad to know that half a cup of kernels provides two grams of filling protein. Corn is also a largely GMO crop.

Eggs
Eggs: King of food protein is the humble egg. A medium egg has around 6g of protein of the highest biological value, meaning it comes complete with all 20 amino acids in the most digestible form. Preferably soft boiled eggs or even raw if you can get certified organic barn-fresh eggs. Although the egg yolk has the highest levels of protein, it is recommended you eat the egg whole as egg white counter-balances the negative effects of the yolk. 6g of protein / per egg

Fish and Seafood
Fish & Seafood: salmon, tuna, haddock, swordfish, orange roughly, crab, lobster, shrimp. Fish and seafood are good sources of protein and are typically low in fat. While slightly higher in fat than other varieties, salmon packs in heart-healthy omega-3 fatty acids.

Milk
Milk packed with protein and contain bone-building calcium, too. Chocolate milk is the age-old recovery food after exercise, since it contains energy-replenishing carbohydrates and a blend of both slow and fast release whey and casein proteins. You can get the same recovery-boosting effects from a milk-based fruit smoothie

Yogurt
Yogurt is a combination of casein and whey protein, yogurt is a great protein-rich food. Since most of the lactose is removed, it can work for most people who are lactose intolerant
Greek yogurt 10g of protein / per 100g

Cottage Cheese
Cottage cheese. Cottage cheese provides amino acids, which your body can use to make these new proteins. It is also a source of complete protein, which means that it provides all the amino acids your body needs to function but cannot synthesize itself. Consuming complete protein sources like cottage cheese helps reduce your risk of an amino acid deficiency, which can impact your cells’ ability to make the proteins it needs to survive. Each cup of large-curd cottage cheese contains around 23 grams of protein, while an equivalent serving of small-curd cottage cheese contains approximately 25 grams.

Poultry
Poultry: chicken breast, turkey breast, lean ground turkey. When it comes to animal protein, opt for lean protein from white meat poultry such as chicken and turkey. It’s wise to discard the skin, which is packed with saturated fat.

Lean Meats
Lean Meats: round steak, sirloin steak, lean ground beef, pork, buffalo. High-quality proteins also contain branched-chain amino acids(BCAAs), which are key in supporting muscle recovery. Leucine, in particular, makes up one-third of muscle protein and helps to stimulate repair after exercise. Pork is one of the richest sources of leucine and, therefore, a great addition to a post-exercise meal or snack. Eggs, chicken, and lean beef also provide good amounts of leucine.
NOTE: Avoid processed meats which include bacon, sausage, hot dogs, sandwich meat, packaged ham, pepperoni, salami and virtually all red meat used in frozen prepared meals. The World Cancer Research Fund (WCRF) has completed a detailed review of more than 7,000 clinical studies covering links between diet and cancer. Bottom line: Processed meats are too dangerous for human consumption. Consumers should stop buying and eating all processed meat products for the rest of their lives.
Protein or Nutrition Bars
Protein or Nutrition bars are heat processed foods and contains lots of sugar and therefore not really healthy. Many of these protein bars contain at least 30 grams of sugar. Bars with soy protein isolate, high fructose corn syrup, Fractionated/hydrogenated palm kernel oil, Artificial sweeteners, BHT: Butylated hydroxytoluene, “Natural flavourings” and other artificial ingredients should be avoided. Most of the protein bars are marketed as “diet” “weight loss” “diabetic” “healthy snacks” etc.

NOTE: Avoid GMO (Genetically Modified Organisms) crops and products made from these bio-tech crops like
- Alfalfa (Medicago sativa)
- Argentine Canola (Brassica napus)
- Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris)
- Carnation (Dianthus caryophyllus)
- Chicory (Cichorium intybus)
- Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.)
- Creeping Bentgrass (Agrostis stolonifera)
- Flax (Linum usitatissumum L.)
- Maize (Zea mays L.)
- Melon (Cucumis melo)
- Papaya (Carica papaya)
- Petunia (Petunia hybrida)
- Plum (Prunus domestica)
- Polish canola (Brassica rapa)
- Poplar (Populus sp.)
- Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.)
- Rice (Oryza sativa L.)
- Rose (Rosa hybrids)
- Soybean (Glycine max L.)
- Squash (Cucurbita pepo)
- Sugar Beet (Beta vulgaris)
- Sugarcane (Saccharum sp)
- Sweet pepper (Capsicum annuum)
- Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.)
- Tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum)
- Wheat (Triticum aestivum)
or contains ingredients that are GMO. Always insist on organic ingredients.
Also, make sure they do not have artificial preservatives, sweeteners, flavors etc. Always insist they are manufactured from organic ingredients.
For animal products, check if the animals are humanely reared and not subjected to chemicals like growth hormones, antibiotics etc especially in chicken and cows. Some factory farmed animals may also be genetically modified.

The Best Protein Powders
Protein powders are used as:
- Meal Replacement (to lose weight)
- Post Workout (build muscle, stamina)
WHEY PROTEIN
- pros:
– quick absorbing (great for post-workout)
– inexpensive
– many flavors available - cons:
– contains lacto
– some brands may contain artificial ingre - Choose this if: You simply want the best powder to increase your protein intake or are looking to build or maintain muscle.
EGG WHITE PROTEIN
- pros:
– rich in vitamins and minerals
– slow absorbing (great for
anytime of the day) - cons:
– common allergen (eggs)
– one of the most expensive - Choose this if: You’re allergic to or don’t eat dairy (e.g. Paleo dieters), but still want a high-quality complete protein.
CASEIN PROTEIN
- pros:
– similar to whey, but is slow absorbing (perfect before bed or anytime of the day) - cons:
– more expensive than whey
– allergen (milk)
– not good for post-workout due to slow absorption
– may clog respiratory system - Choose this if: You generally use protein powder as a meal replacement or before bed, or if you want to combine it with whey for optimal muscle-building effects.
SOY PROTEIN
- pros:
– may improve immune system
– may promote bone health
– may prevent cardiovascular diseases and reduce the risk of certain cancers - cons:
– often genetically modified (GMO)
– may have an effect on hormone levels - Choose this if: You’re vegan and want the best plant-based complete protein to help build muscle, stay full, or simply reach your daily protein quota.
RICE PROTEIN
- pros:
– good source of complex carbs, vitamin B, and fiber.
– hypoallergenic - cons:
– deficient in some amino acids
HEMP PROTEIN
- pros:
– superfood
– contains 21 amino acids
– hypoallergenic
– high in fiber - cons:
– often the most expensive - Choose this if: You want to ramp up your overall nutrient intake and don’t have strong protein needs.
PEA PROTEIN
- pros:
-hypoallergenic
-easily digestible
-few additives or artificial ingredients - cons:
-deficient in certain amino acids
- Choose this if: You avoid animal-derived products, but don’t want to eat soy, or if you have digestive issues.
VEGAN PROTEIN
- pros:
– gluten-free, dairy-free, soy-free
– does not cause stomach upset
– great for vegetarians - cons:
-bit more expensive
BROWN RICE PROTEIN
- pros:
– nearly same benefit as whey and rice protein - cons:
– low in certain amino acids like lysine

WHY WHEY PROTEIN?
Avoid the threat of weakened muscles and fragile bones.
BUILD A LASTING LEAN BODY FOUNDATION
Muscle retention has little to do with looking good in a swimsuit, and everything to do with your health and longevity. Age related muscle loss is called sarcopenia, and you will live a much healthier life if you work to
prevent its effects,
Sarcopenia impacts all of us – including you. Muscle mass peaks around 30 years old, and from age 30 to 60, adults lose approximately half a pound of muscle and gain around one pound of fat per year. So sarcopenia is often accompanied by unhealthy fat gain. Losing muscle and putting on fat is a double-edged sword. Each has its own harmful effects, which together can have serious consequences for your health.
THE SCIENCE OF “FIT”
In a nutshell, our bodies use fat as a reserve. Think of fat like your body’s “emergency supply.” Vou should store some extra in case a catastrophe prevents you from ingesting any nutrients or calories, but any excess hinders your body’s optimal function. Fat gain that exceeds our body’s normal reserves can begin to build up around our organs, This results in what’s called “visceral fat” which lies deep within our bodies, building up around vital organs and posing a major risk
to our health,
Along with gaining fat, losing muscle has also been shown to compromise health and increase risk of disease. Maintaining muscle helps to banish bad fat and supports joint, tissue, immune and heart health. Additionally, muscle mass supports a healthy metabolism and can help with weight-loss goals. A study by Maastricht University Medical Center revealed a single daily dose of 35 grams of whey protein led to higher circulating levels of amino acids, as well as improved muscle synthesis. The “right” kind of protein nourishes your whole body and gets rid of unhealthy fat that can build up as you age, from the inside out.
PROTEIN HELPS YOU KEEP MUSCLE
Keeping muscle as you age helps guard against conditions associated with aging. Muscle is the superhero in the fight against the “bad guy” sarcopenia.
The Journal of the American Medical Association explains, “Sarcopenia is the backdrop against which the drama of disease is played out.” If you’re not getting enough protein, your body can’t fight illness or degeneration. Even if your body weight is normal, having a high percentage of body fat puts you at an increased risk for chronic disease.
Beware of Some Protein Powders
Organic whey protein should be high on your priority list of protein to be consumed on a daily basis. Check this nutritional study done by JN ( Journal of Nutrition) on why you should be taking whey protein most.

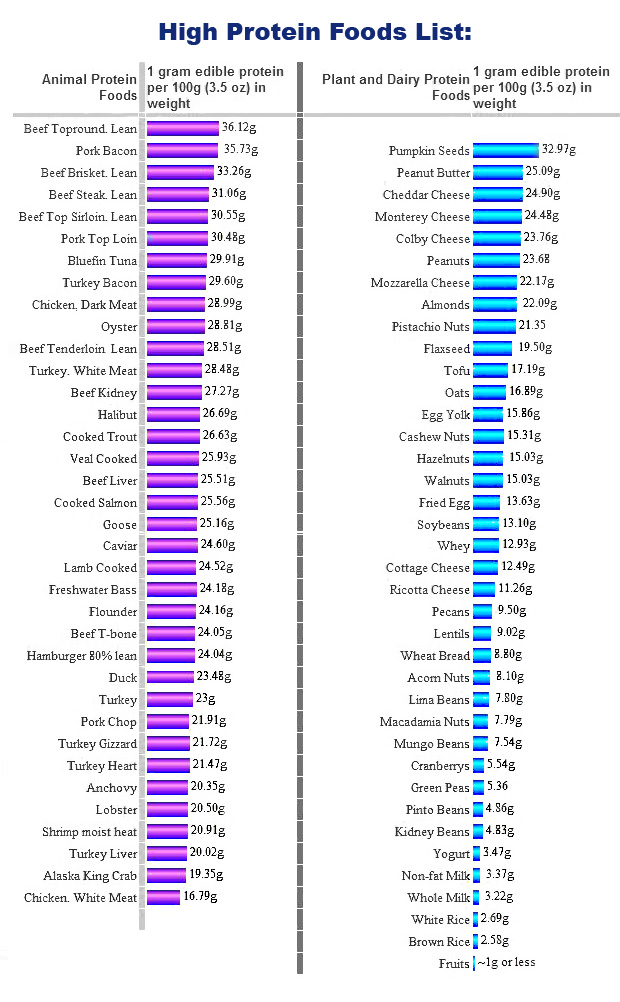
The list below gives a comparison list of Animal Protein Foods and Plant and Dairy Protein Foods. It is important to balance our intake of protein foods with essential fats and complex carbohydrates. It will be useful for people who want to slim down and lose weight: We need to consume about 50 – 60 grams of protein food per day. This works out to about 8 ounces, or 225 grams of meat per day. People who are physically active may need to have a high intake of proteins. As can be seen from the table below, plants are also high in proteins and are a good source of proteins from breakfast to dinner and even snacks if eaten in the right proportion / combination.
Related Articles:
ORGANIC FOOD SHOPPING PRIORITY LIST
© https://teamrich.wordpress.com – Best High Protein Foods
Protein has completely surpassed our expectations. I like protein more and more each day because it makes my life a lot easier. To be honest you cannot beat the services or the people that I have dealt with.
can you please send to my email (normamauras@yahoo.com) more information about high protein food. Thank you
1. Sorry we don’t have the facilities to email info.
2. you can follow us on Facebook (lookup “nancy.long.sg” and add me as a friend. We publish a lot of article there.
3. subscribe to our RSS
Thanks for your interest
nice blog bro
What if people wants to gain weight and they barely have proteins ? Should they also eat the same stuff above the list to gain for protein ?? Please let me know asap!!
Great article.